Children’s Orthodontic Treatment: What to Expect and When to Start
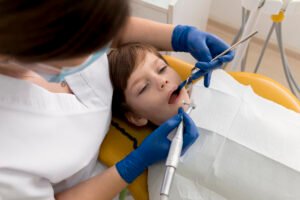
When we think of orthodontics, we often picture teenagers with braces. However, Children’s Orthodontic Treatment can have a significant impact on a child’s dental health.

When we think of orthodontics, we often picture teenagers with braces. However, Children’s Orthodontic Treatment can have a significant impact on a child’s dental health.

Gaps between teeth, is a common dental concern that affects both children and adults. While some people embrace their gapped smile as a unique feature,

Do you experience discomfort when eating ice cream or drinking hot coffee? If so, you’re not alone! Tooth sensitivity affects millions of people, but the

Cavities in children are a common concern for parents, but the good news is that they can be prevented with proper care and habits. According

When it comes to achieving a healthy, confident smile, choosing the right orthodontic provider is key. If you’ve been searching for “orthodontics near me,” you’re

As parents, it’s natural to want to bond with your baby during mealtime. However, sharing utensils with your baby could have unintended consequences for their

©Copyright Zipper Orthodontics 2024 – Braces & Invisalign in Boynton Beach and Boca Raton, FL
Looking for an orthodontist near me in Boynton Beach and Boca Raton, FL? Orthodontist Dr. Brandon Zipper at Zipper Orthodontics specializes in state of the art braces, metal braces, clear braces, ceramic braces, sleep apnea, itero digital impressions, and Invisalign. We also offer early orthodontic treatment for children, and full orthodontic treatment for teens, and adult orthodontics. When considering your investment which includes the cost of braces, the cost of Invisalign, and the time it takes to create your new smile, you can’t put a price tag on a life-changing appearance which improves your long term dental health.
Visit our two convenient locations today in Boynton Beach and Boca Raton, FL. You will see for yourself orthodontist Dr. Zipper and his team offer effective and affordable braces serving Lake Worth 33460 and Delray Beach 33444, FL.